
Material management plays a vital role in ensuring smooth production and efficient operations across industries. It involves the planning, procurement, storage, movement, and control of raw materials, components, and finished goods. Effective material management ensures that the right material is available at the right time, in the right quantity, and at the right cost.
For professionals aspiring to build a career in supply chain and production, a PG Diploma in Material Management or Post Graduate Diploma in Material Management provides in-depth knowledge of these processes. Let’s explore the steps, types, objectives, and importance of the material management process in detail.
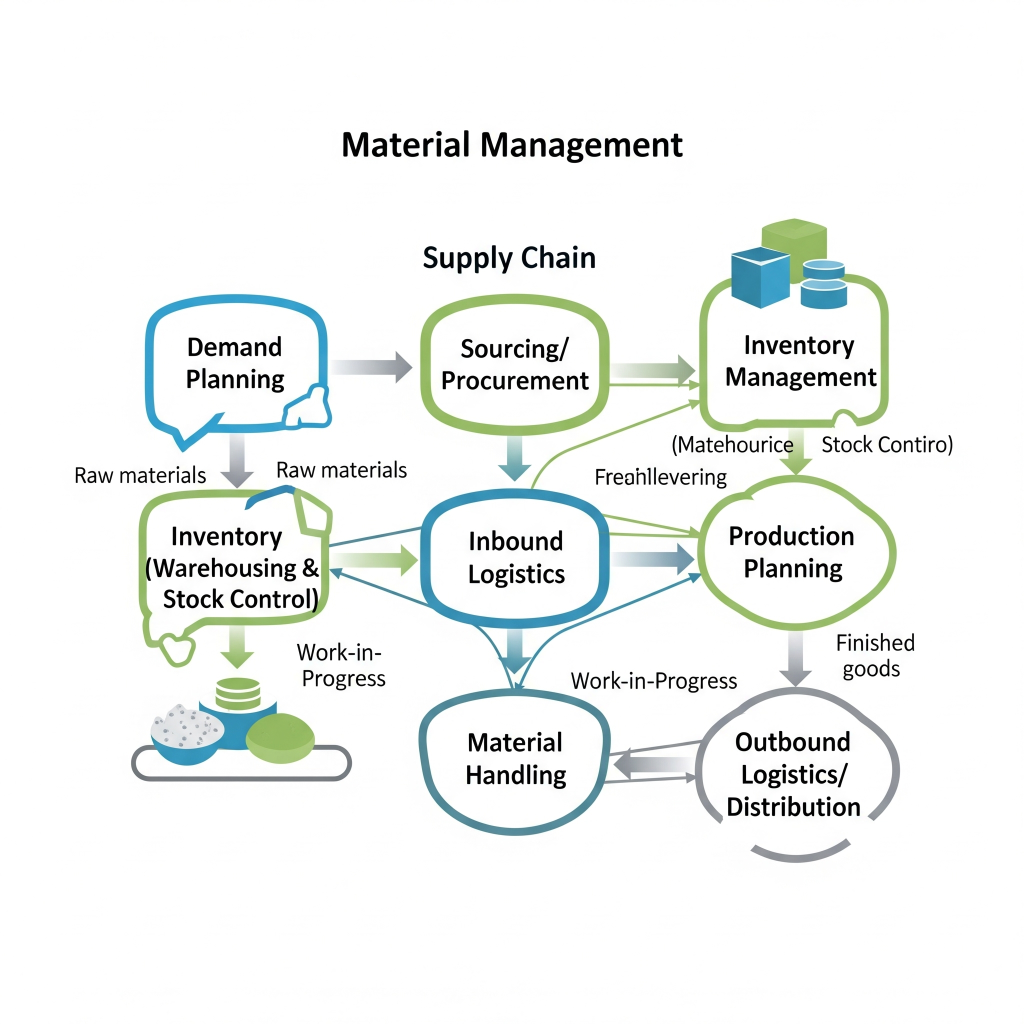
What is the Material Management Process in Supply Chain?
In the supply chain, material management is the backbone that connects suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. It ensures the smooth flow of raw materials into production and finished goods to the market.
The material management process in the supply chain involves:
- Identifying material requirements
- Planning procurement
- Negotiating with suppliers
- Ensuring timely deliveries
- Maintaining optimum inventory levels
- Managing warehouses and distribution
In short, it is the bridge between procurement and production, making the entire supply chain more cost-effective and reliable.
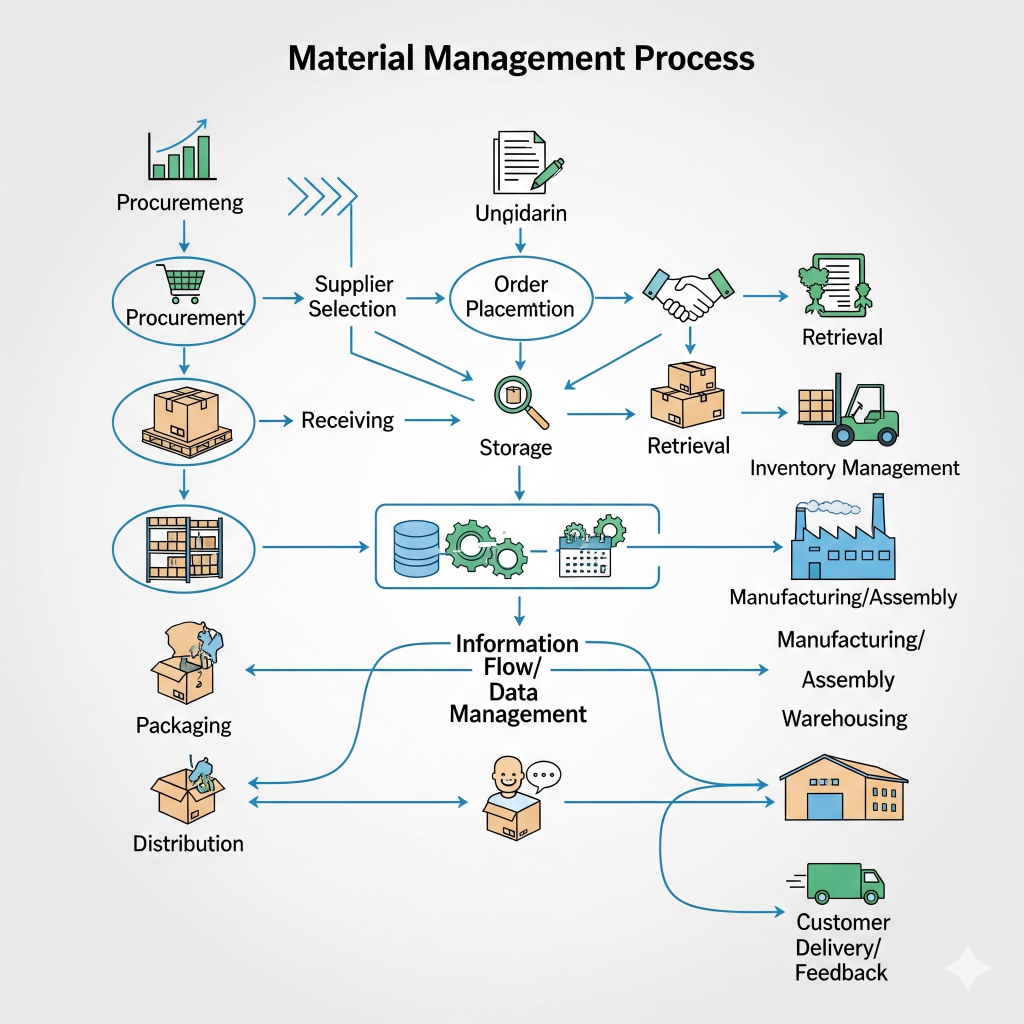
Steps Involved in the Material Management Process
The material management process can be broken into structured steps that organizations follow:
- Material Requirement Identification – Analyzing what materials are needed for production.
- Planning & Scheduling – Deciding when and how much material should be purchased.
- Procurement – Selecting vendors, negotiating, and purchasing raw materials.
- Receiving & Inspection – Checking quality and verifying quantities received.
- Storage & Inventory Control – Storing materials safely and maintaining accurate stock records.
- Issuance to Production – Supplying materials to manufacturing as per demand.
- Waste Reduction & Returns – Managing scraps, reusing materials, and returning unused stock.
Material Management Process Types
The material management process can be categorized into different types based on focus areas:
- Purchase Management – Deals with sourcing and procurement of materials.
- Inventory Management – Involves maintaining optimum stock levels.
- Logistics Management – Ensures smooth transportation and distribution.
- Production Material Management – Supplies materials efficiently to production units.
- Waste Management – Reduces wastage and promotes material reuse.
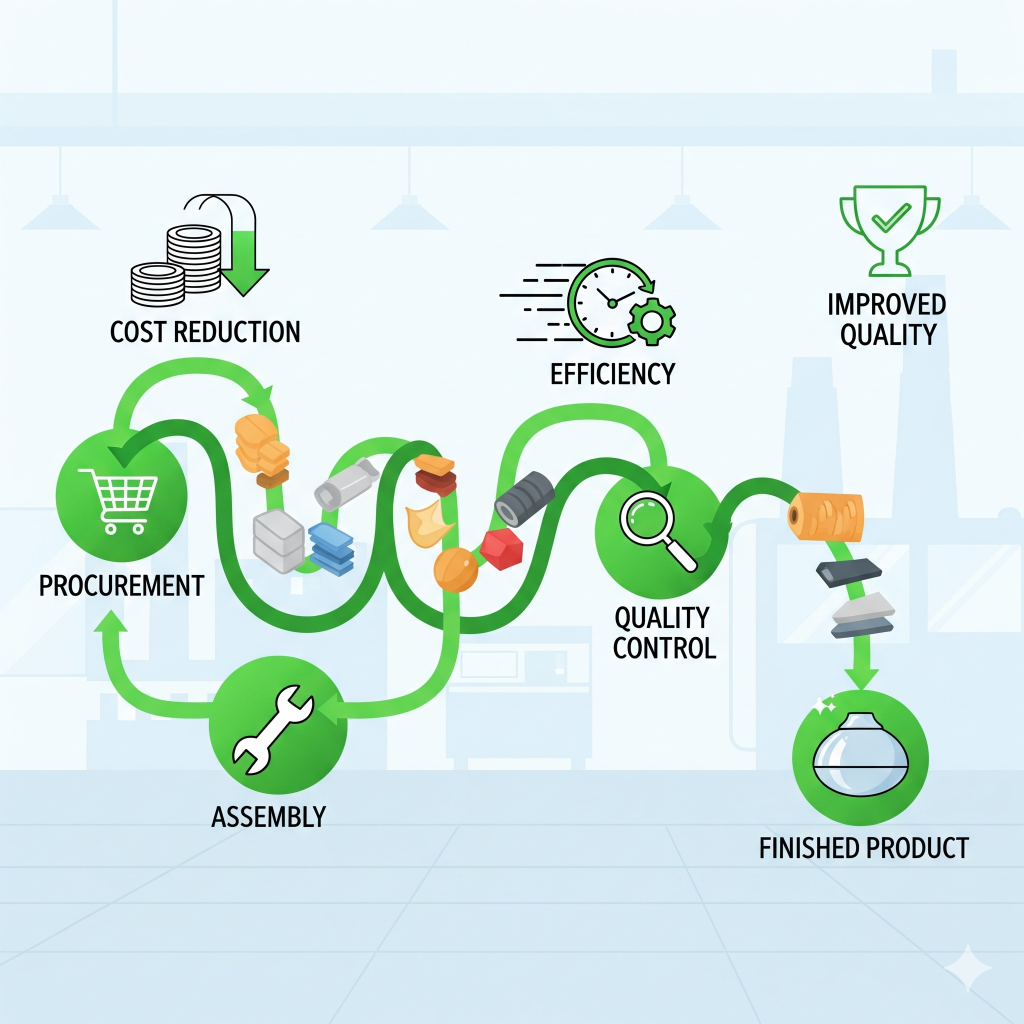
Importance of Material Management in Production Process
Material management ensures uninterrupted production by making the right materials available at the right time. Its importance includes:
- Avoiding stockouts and delays
- Maintaining product quality by sourcing good raw materials
- Reducing wastage and controlling production costs
- Enhancing customer satisfaction with timely deliveries
- Optimizing resource utilization across operations
For manufacturing companies, poor material management can lead to production halts, cost escalations, and dissatisfied customers.
Objectives and Functions of Material Management Process
The key objectives of material management are:
- Cost Reduction – Buy materials at the lowest total cost.
- Uninterrupted Supply – Ensure continuous flow of materials to production.
- Quality Control – Source high-quality materials.
- Efficient Inventory – Maintain optimum stock levels.
- Vendor Management – Build strong supplier relationships.
Its main functions include purchasing, inventory control, standardization, transportation, warehousing, and disposal of obsolete materials.
Material Management Process in Manufacturing Industry
In manufacturing, material management directly impacts productivity and profitability. Every production cycle depends on the availability of raw materials, components, and consumables. A well-planned material management system ensures:
- Raw materials are available as per the production schedule
- Inventory costs are minimized
- Dead stock and wastage are reduced
- Supply chain disruptions are prevented
Thus, material management is not just a support function but a strategic tool in the manufacturing industry.
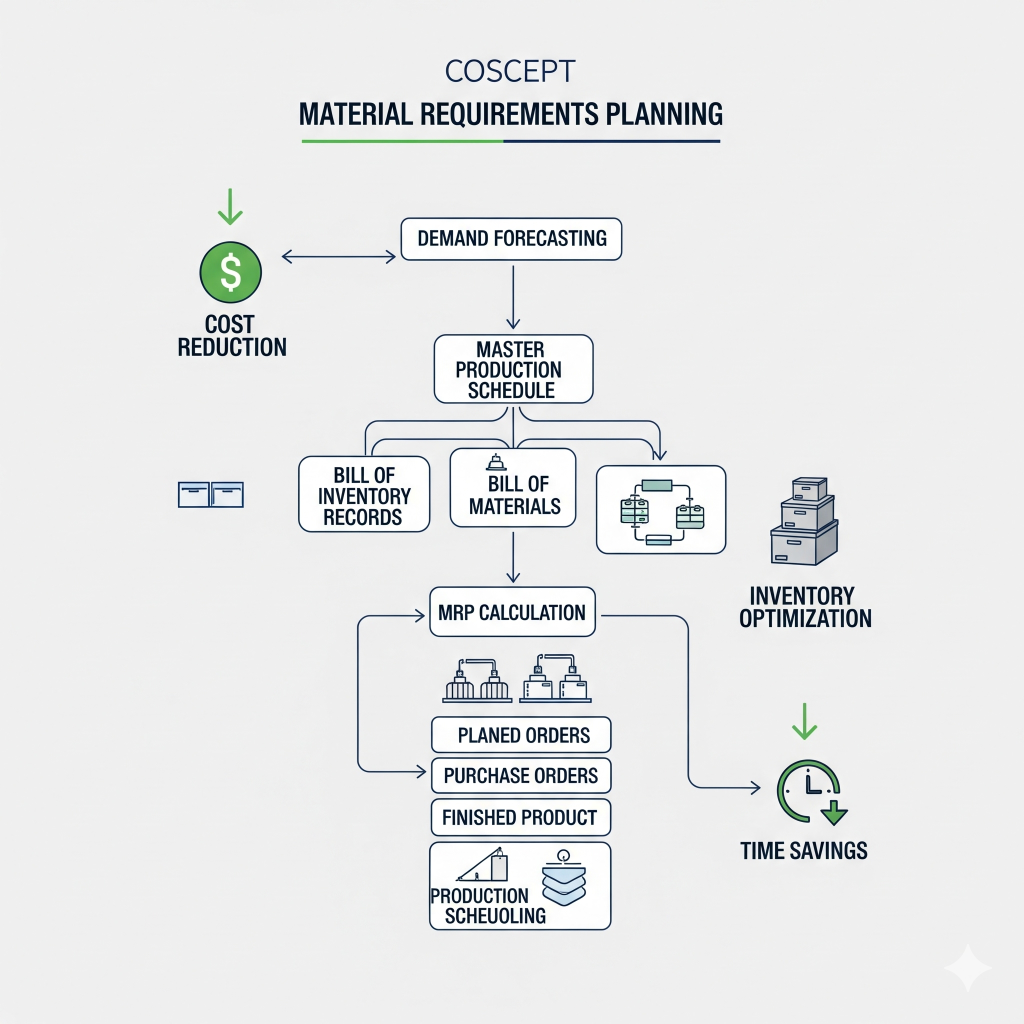
Material Requirement Planning in Material Management
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a computerized system that ensures the right quantity of materials is available for production.
It uses:
- Production schedules
- Inventory records
- Bill of materials (BOM)
MRP helps managers forecast material needs, plan purchases, avoid excess inventory, and optimize resources. It is one of the most widely used tools in modern material management.
How Material Management Improves Cost Efficiency
An effective material management process contributes to cost savings in multiple ways:
- Reduces storage and handling costs by avoiding overstocking
- Minimizes wastage through better inventory control
- Ensures bulk purchasing and better vendor negotiations
- Prevents production downtime due to shortages
- Optimizes logistics and reduces transportation expenses
Efficient material management is a direct path to higher profitability.
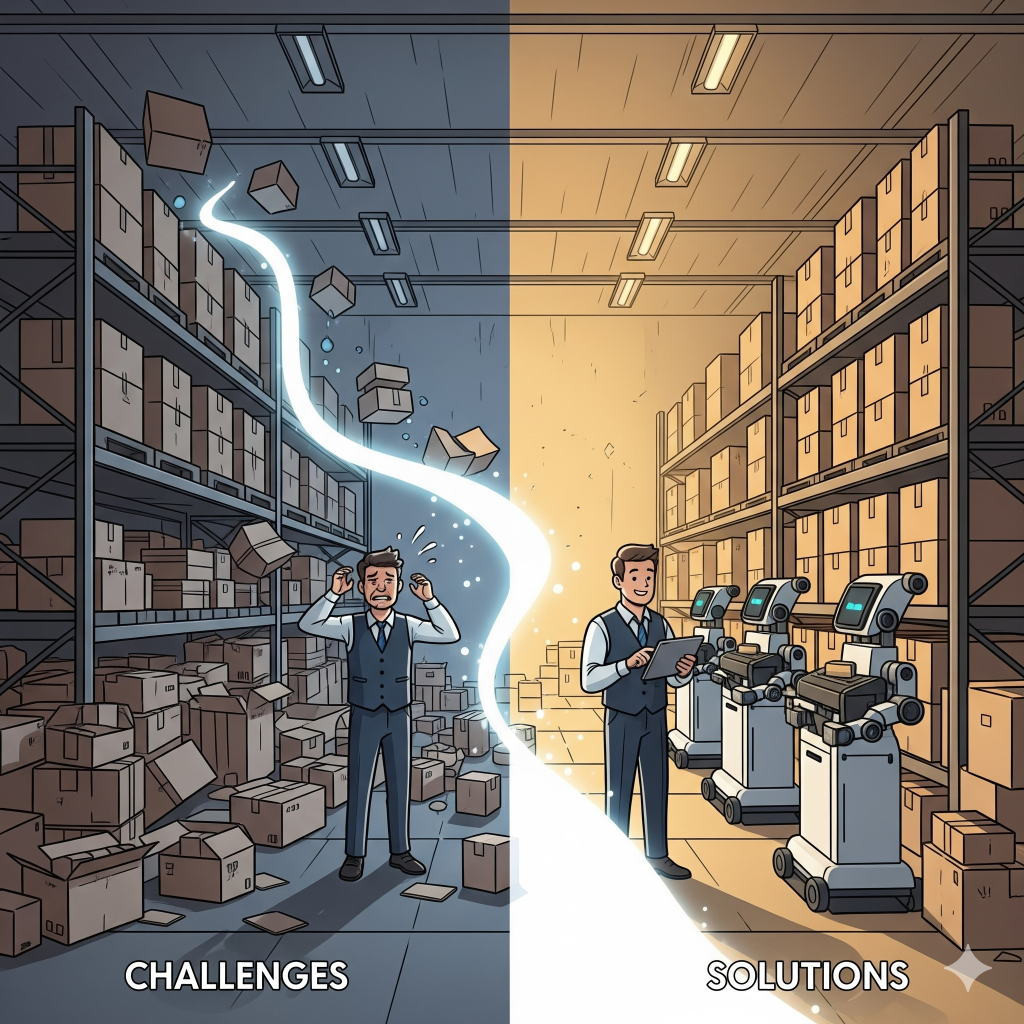
Challenges in Material Management Process and Solutions
While material management is crucial, it comes with challenges such as:
- Demand Forecasting Issues – Uncertain market demand can disrupt planning.
Solution: Use data analytics and forecasting tools. - Vendor Reliability – Delays from suppliers affect production.
Solution: Build long-term vendor relationships. - Excess Inventory – Leads to storage costs and material obsolescence.
Solution: Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) systems. - Quality Problems – Poor raw materials lead to defective products.
Solution: Strict quality checks at procurement and receiving stages.
Best Practices for Effective Material Management Process
Organizations can achieve efficiency by following these best practices:
- Adopt modern tools like ERP and MRP systems.
- Use data-driven demand forecasting.
- Maintain strong supplier partnerships.
- Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) practices.
- Regularly review inventory policies.
- Train staff in material handling and cost control.

Procurement and Material Management Process Explained
Procurement is the first step of material management. It involves sourcing, negotiating, and purchasing the required raw materials. Once procured, material management takes over to ensure proper storage, control, and timely movement to production.
In other words:
- Procurement = Acquiring materials.
- Material Management = Planning, controlling, and utilizing those materials efficiently.
Both are interconnected but serve different purposes.
Difference Between Material Procurement and Material Management
Aspect | Material Procurement | Material Management |
Definition | Process of purchasing raw materials | Process of planning, controlling, and utilizing materials |
Focus | Sourcing and buying | Storage, inventory, and usage |
Objective | Acquire materials at the best price | Optimize cost, reduce waste, and ensure production flow |
Scope | Limited to purchasing | Covers procurement, inventory, storage, and movement |
Procurement is just one part of material management, while material management is a broader and more strategic process.
Conclusion
The material management process is the backbone of supply chain and production efficiency. It involves multiple steps, from planning and procurement to storage, distribution, and waste reduction. By ensuring the right materials reach production at the right time, material management helps reduce costs, improve quality, and enhance productivity.
For those looking to build expertise in this field, pursuing a PG Diploma in Material Management or a Exec. Post Graduate Diploma in Material Management can provide the necessary skills and industry-oriented knowledge. With growing demand for supply chain and production specialists, material management offers rewarding career opportunities in manufacturing, logistics, and beyond.


