In today’s fast-paced global economy, logistics and supply chain management have become crucial pillars of business success. Yet, many aspiring professionals and even business owners often confuse the two. While they are closely interrelated, supply chain management and logistics management differ in scope, function, and strategic importance.
If you are considering supply chain management courses in India, understanding these differences will help you make an informed choice and choose the right specialization for your career goals.
Understanding Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) refers to the end-to-end coordination of the flow of goods and services from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to customers. It encompasses a network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and end consumers.
Key Stages in SCM
- Planning: Forecasting demand and allocating resources efficiently.
- Sourcing: Procuring raw materials and components from reliable suppliers.
- Manufacturing: Converting raw materials into finished products.
- Logistics: Managing warehousing, transportation, and inventory.
- Delivery: Ensuring timely product distribution.
- Returns: Handling reverse logistics for returned goods.
Goals of Supply Chain Management
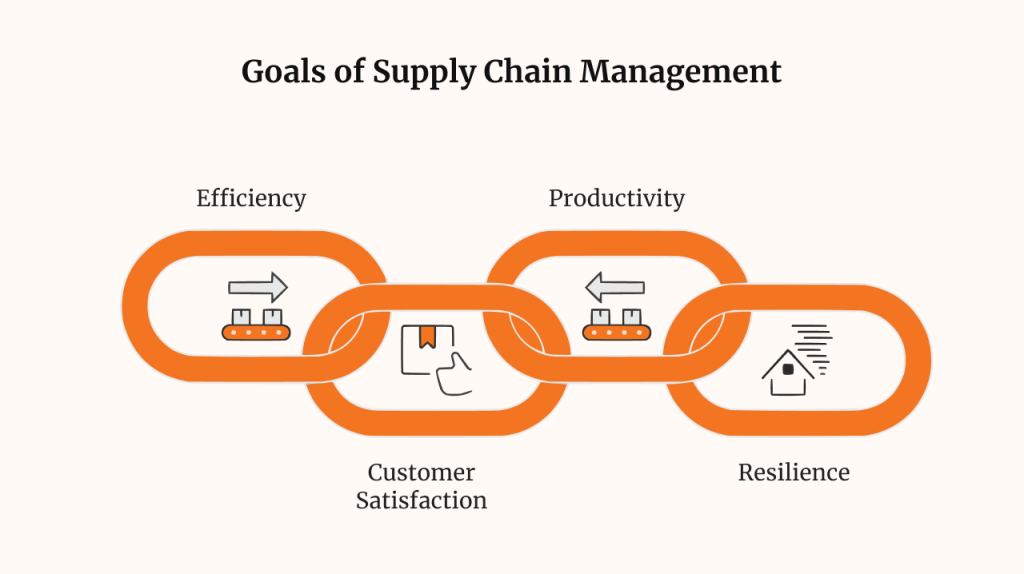
- Efficiency: Streamlining operations to reduce waste and costs.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring product availability and timely delivery.
- Productivity: Optimizing use of manufacturing and logistics assets.
- Resilience: Building flexible systems to handle disruptions and market shifts.
Modern Trends in SCM
- Technology Integration: Using AI, blockchain, and cloud platforms for data visibility and automation.
- Sustainability: Emphasizing eco-friendly and ethical sourcing practices.
- Customer-Centric Models: Moving from linear systems to responsive, demand-driven networks.
Understanding Logistics Management
Logistics Management is a subset of SCM that focuses specifically on the movement, storage, and delivery of goods. It ensures that products reach the right place, at the right time, in the right condition—and at minimal cost.
Key Components
- Transportation: Selecting and managing transport modes for efficiency.
- Warehousing: Safe and optimized storage of goods.
- Inventory Management: Maintaining balanced stock levels to meet demand.
- Packaging: Protecting goods during storage and transit.
- Information Flow: Coordinating real-time data exchange for smooth operations.
- Materials Handling: Managing physical movement within facilities.
Core Goals
- Customer Satisfaction: Timely and accurate deliveries.
- Operational Efficiency: Reducing waste and process delays.
- Cost Control: Minimizing expenses without compromising quality.
Importance in Modern Business
In today’s digital economy, logistics plays a critical role in competitiveness. Companies leverage IoT, AI, and predictive analytics to monitor shipments, forecast delays, and improve customer experience.
Key Differences Between Supply Chain and Logistics Management
While logistics management focuses on tactical execution, supply chain management deals with strategic coordination across multiple functions and partners.
Aspect | Logistics Management | Supply Chain Management |
Definition | Managing the flow of goods between origin and consumption points. | Coordinating the flow of goods, services, and information across the entire value chain. |
Scope | Concerned with transportation, warehousing, and inventory. | Encompasses logistics along with planning, sourcing, production, and delivery. |
Focus | Operational and process-driven. | Strategic, collaborative, and outcome-driven. |
Goal | Efficient delivery and cost optimization. | End-to-end efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage. |
Activities | Transportation, warehousing, packaging, order fulfillment. | Planning, sourcing, production, logistics, and customer relationship management. |
In short, logistics management ensures operational efficiency, while supply chain management aligns all functions to achieve organizational excellence.
Pursuing Supply Chain and Logistics Courses in India
With the growing demand for skilled professionals in both domains, many learners are now enrolling in supply chain courses in India to build future-ready careers. These programs help students understand global supply networks, strategic procurement, data-driven logistics, and sustainability practices.
Among top institutes offering supply chain management courses in India with placement, MIT School of Distance Education (MITSDE) stands out for its industry-oriented approach.
Why Choose MITSDE?
- Comprehensive Curriculum: MITSDE offers a wide range of supply chain management courses in India, covering both logistics management and supply chain strategy.
- Flexible Learning: With distance and online learning options, students can upskill without disrupting their careers.
- Expert Faculty: Learn directly from industry professionals and academic experts.
- Placement Support: MITSDE’s programs are designed to ensure career readiness, offering supply chain management courses in India with placement assistance.

MITSDE offers the following programs in this domain:
- PGDM in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
- Executive PGDM in Supply Chain Management
- Professional Certificate in Logistics and Supply Chain
These programs help learners master operations, procurement, logistics strategy, and global supply dynamics—making them ideal for those aspiring to leadership roles in the logistics or manufacturing sectors.
Explore the full range of programs at 👉 MITSDE.com
Final Thoughts
Both logistics management and supply chain management play vital roles in ensuring business continuity and customer satisfaction. While logistics ensures efficient product flow, supply chain management focuses on long-term strategy and collaboration across the value chain.
For professionals aiming to build expertise in these high-demand fields, enrolling in reputed supply chain management courses in India like those offered by MITSDE can open doors to global career opportunities and long-term growth.